Point-to-Network Join and Spatiotemporal aggregations
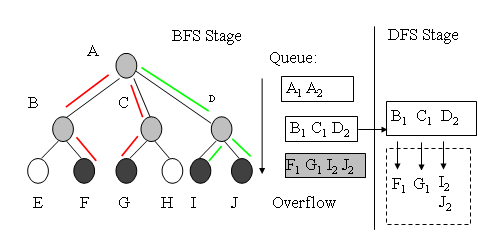 |
R-trees are popular spatial indexing
techniques that have
been widely used in many geospatial applications. The
increasingly available Graphics
Processing Units (GPUs) for general computing have
attracted considerable
research interests in applying the massive data parallel
technologies to index
and query geospatial data based on R-trees. In this
paper, we investigate on the
potential of accelerating both R-tree bulk loading
construction and R-tree
based spatial window query on GPUs. Experiments
show that our proposed GPU-based parallel query
processing implementation achieves
6x~18x speedup over serial CPU implementations and is 2X
faster on average over
8-core CPU implementation using OpenMP. Our experiments
also show that the
speedups are significantly affected by R-tree qualities
which warrants further
investigations. Additional comparisons between the GPU
R-tree implementation and
a GPU single-level grid-file based indexing approach are
performed to
understand the relative advantages and disadvantages of
the two popular spatial
indexing approaches on GPUs. |
1) Jianting Zhang and Simin You (2012). GPU-based Spatial Indexing and Query Processing Using R-Trees . Technical Report [Link]