|
|
|
MAIN CALLS PROCEDURE
Use of STATIC
Example 1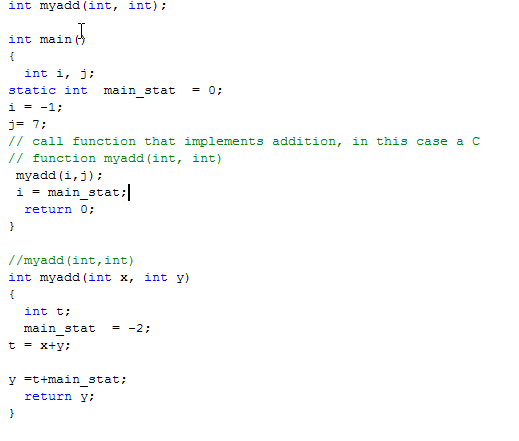
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i after return from myadd();i=main_stat;?
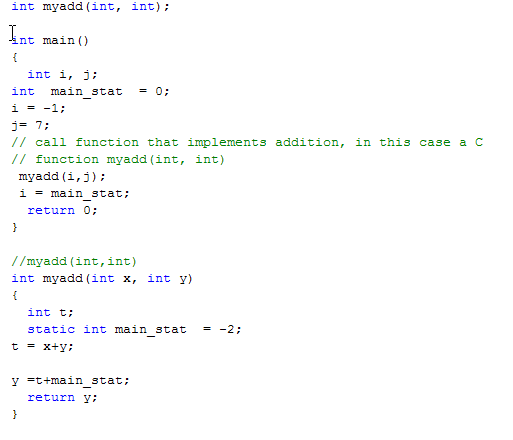
Example 2
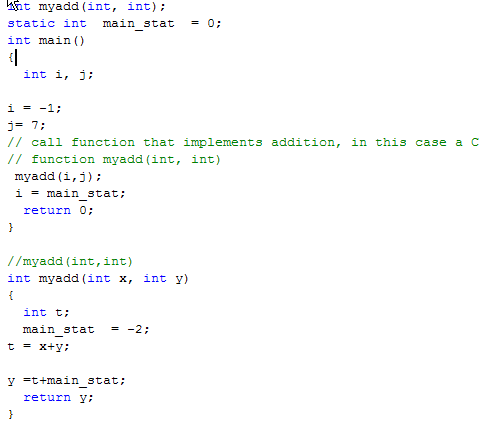
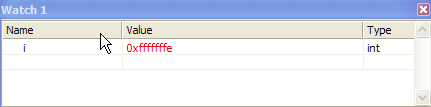
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i after return from myadd();i=main_stat;?
Example 3
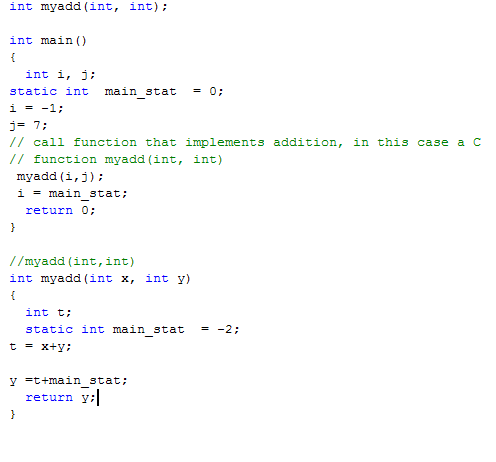
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i after return from myadd();i=main_stat;?
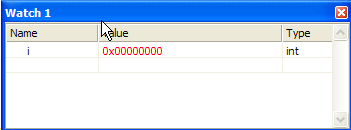
CONCLUSION:
internal static variables provide
private, permanent storage
within a single function.
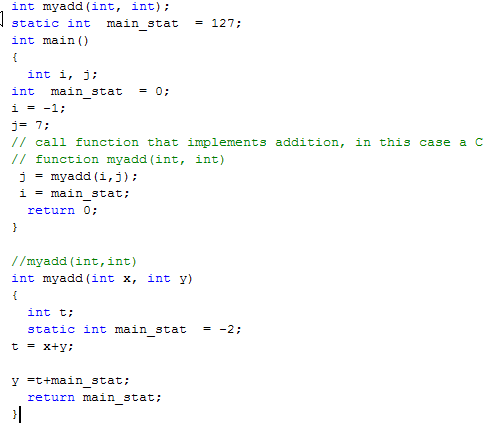
Example 4
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j after return from myadd(); i=main_stat;?

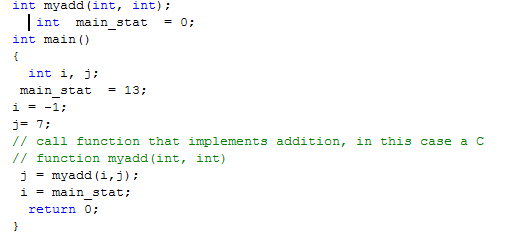
Example 5
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j, main_stat after
return from myadd(); i=main_stat; ?

Main and Procedure are in different files
Example L1
Main is in file
main.ccp
Will it compile without errors?
YES!
Myaad.ccp is given in a separate file

Will it compile without errors?
YES!
Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j, main_stat after
return from myadd(); i=main_stat; ?
Click to see the ouput window in .NET.
Example L2
We can fix it! We leave the main.cpp unchanged and add extern to MyAdd.cpp file:

and in a separate file the procedure MYADD() we add extern:

Will the code compile and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j, main_stat after
return from myadd(); i=main_stat; ?
CLICK HERE TO SEE !
IN DEBUG MODE
NOTE: extern keyword in C++ (or C) declares a variables without
allocating memory (without defininig it!).
It is assumed that the variable will be defined somewhere else.
Initialization of the extern int i= 3;
will allocate memory. any other definition of the same variable in same program (in different files)will result in an error.
Q.: who will detect the error? compiler, linker, processor at run-time,
good programmer, average programmer.
main_stat is a global variable.
Example L2
static local variable
is used when the value of that variable must
persists across different invocations.
Question: why regular local variables can not be used?
answer: static local variables
funct()
{
....
static int variable = -1;
.....
}
Example L2
GLOBAL name
- is defined in one file and used in multiple files
static GLOBAL name
- is used when we want the value of that variable be
invisible ( private to) the file in which it is defined.
(S.B. Lippman, C++ Primer, page 125.)
So there is no NAME conflict if it is used in other files!!
Question: why regular ( not static) variables can not be used?
answer: Please look previous example L2.
Lets look into the next example:
Example L 3
Now we want to make the int main_stat private to the main.cpp file only. Can we do it??? In other words can we make main_stat invisible to the precedure myaddd() which is in another file???
YES!!! we can!
static int main_stat
in The file
MyMain.cpp

Now we try to use it in function mayadd() which is in the file MyAdd.cpp

Now we ask the same question
Will the code compile, link and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j, main_stat after
return from myadd(); i=main_stat; ?
Example L4
To fix the Linker problem: remove extern in MyAdd.cpp file
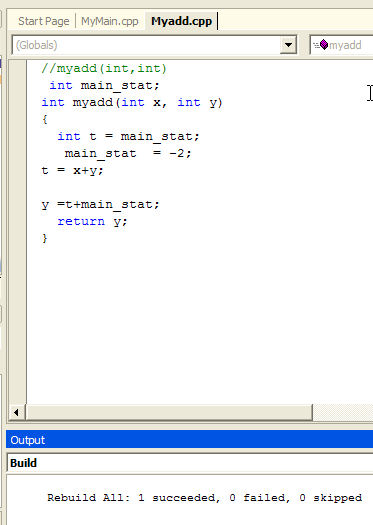
Now Compile and Link the Main.cpp
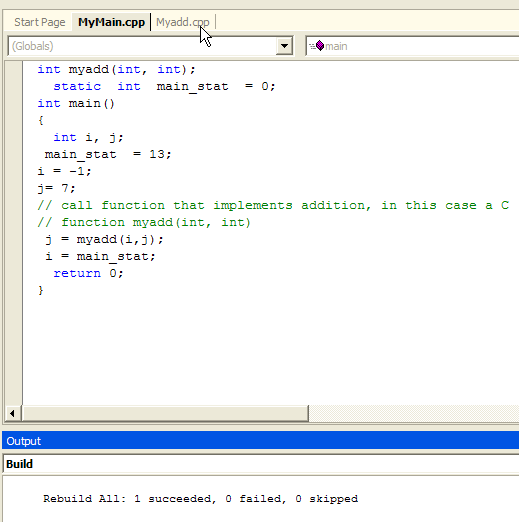
Will the code compile, link and run with no errors?
If yes, then WHAT is the value of variable i,j, main_stat after
return from myadd(); i=main_stat; ?
CLICK HERE!















